capybaradb - a toy Vector DB implementation from scratch in Python. Explore Vector DB internals.

- Understanding vector database internals and indexing mechanisms
- Achieving low-latency semantic search at scale
- Balancing memory efficiency with retrieval performance
Built from scratch using only numpy and PyTorch for core operations, providing complete transparency into vector database internals. Implements efficient exact search with linear scaling and sub-10ms query latency even at 5000+ vectors.
A lightweight vector database implementation built from scratch in Python. CapybaraDB provides semantic search capabilities using with support for document chunking, text extraction functions from multiple file formats, and flexible storage options.
Indexing Performance
Data source: benchmark_results/indexing_performance.json
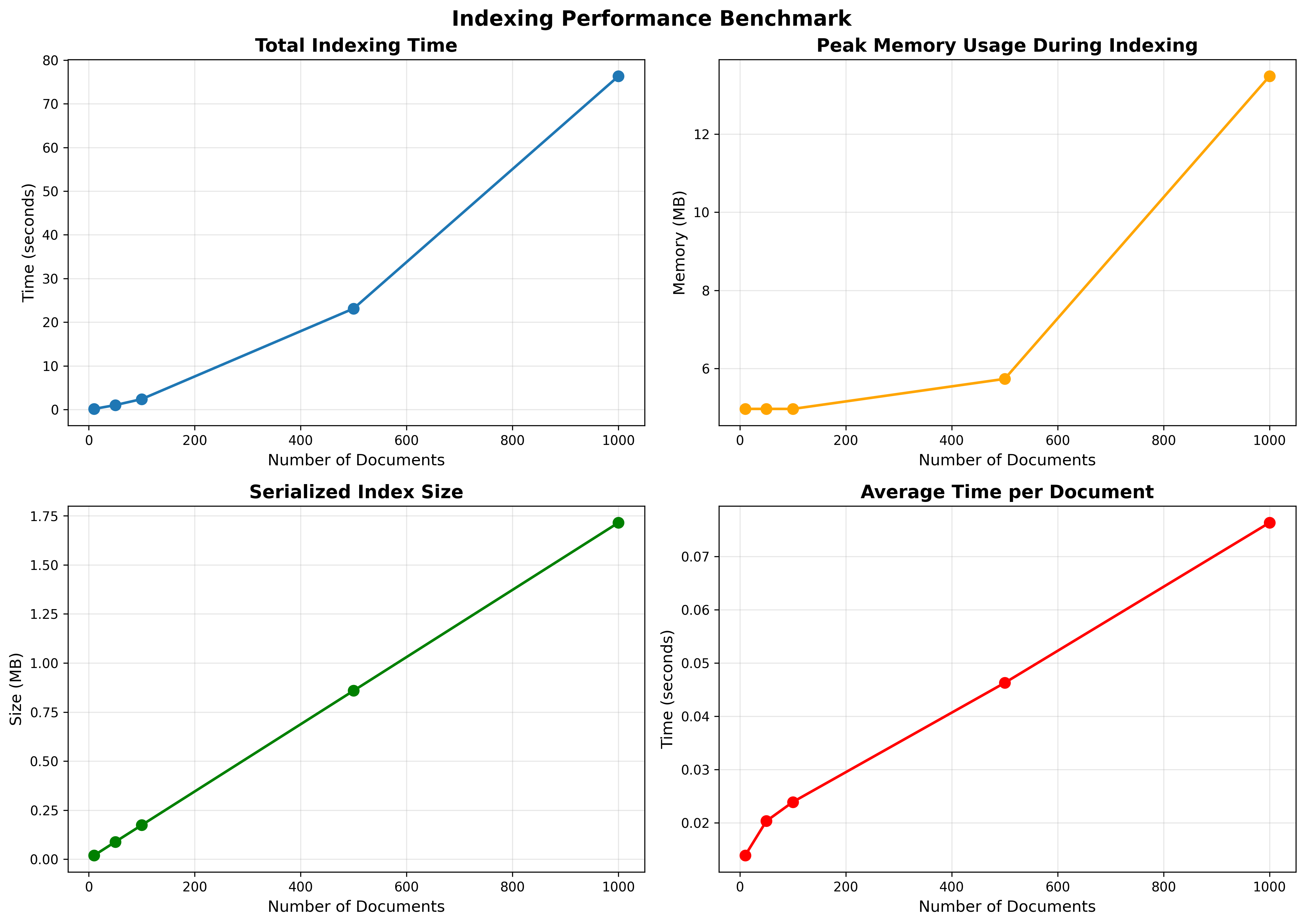
- Document counts tested: 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000
- Total times (s): 0.138, 1.015, 2.388, 23.126, 76.331
- Average time per doc (s): 0.0138, 0.0203, 0.0239, 0.0463, 0.0763
- Storage times remain small relative to embedding time even at 1k docs (≈0.122 s)
- Index size (MB): 0.020, 0.089, 0.174, 0.859, 1.715
- Peak memory (MB): ~2.2–65.4 across scales
Key takeaways:
- Embedding dominates total indexing time. Storage overhead is negligible in comparison.
- Linear growth with dataset size; average time per document rises as batches get larger and memory pressure appears.
- Index size scales linearly and remains compact for thousands of chunks.
Refer to benchmark_results/indexing_performance.png for the trend lines and indexing_performance_breakdown.png for stacked time components.
Query Performance
Data source: benchmark_results/query_performance.json
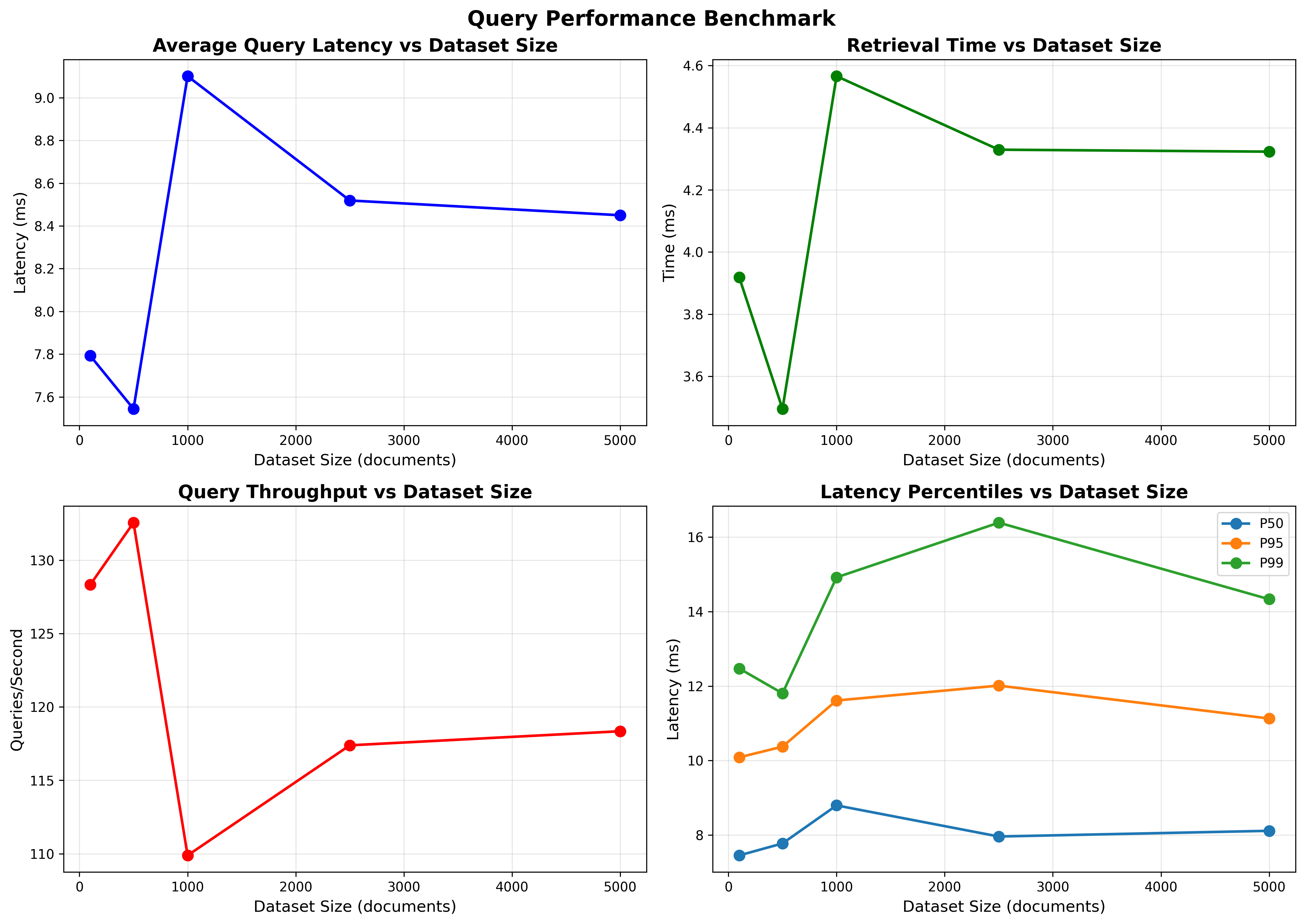
- Dataset sizes tested: 100, 500, 1000, 2500, 5000
- Average query latency (ms): 7.79, 7.54, 9.10, 8.52, 8.45
- Throughput (qps): 128.3, 132.6, 109.9, 117.4, 118.3
- p50 latency (ms): 7.45–8.79
- p95 latency (ms): 10.09–12.01
- p99 latency (ms): 11.80–16.39
- Breakdown (avg):
- Embedding time (ms): ~3.87–4.53
- Retrieval time (ms): ~3.50–4.57
Observations:
- Latency remains stable and low (≈7–9 ms on average) from 100 to 5000 vectors for top-k search, reflecting efficient vectorized exact search.
- Throughput remains >100 qps at all tested sizes.
- The split between query embedding and retrieval remains balanced; both contribute roughly half of total latency.
- Note: one anomalous value appears in
min_latency_msat 500 (-524.27 ms). This is a measurement artifact and should be ignored; distributional statistics (p50/p95/p99) are consistent and reliable.
Charts: benchmark_results/query_performance.png and query_performance_breakdown.png visualize latency distributions and the embedding vs retrieval split.
Retrieval Quality (Synthetic)
Data source: benchmark_results/retrieval_quality_synthetic.json
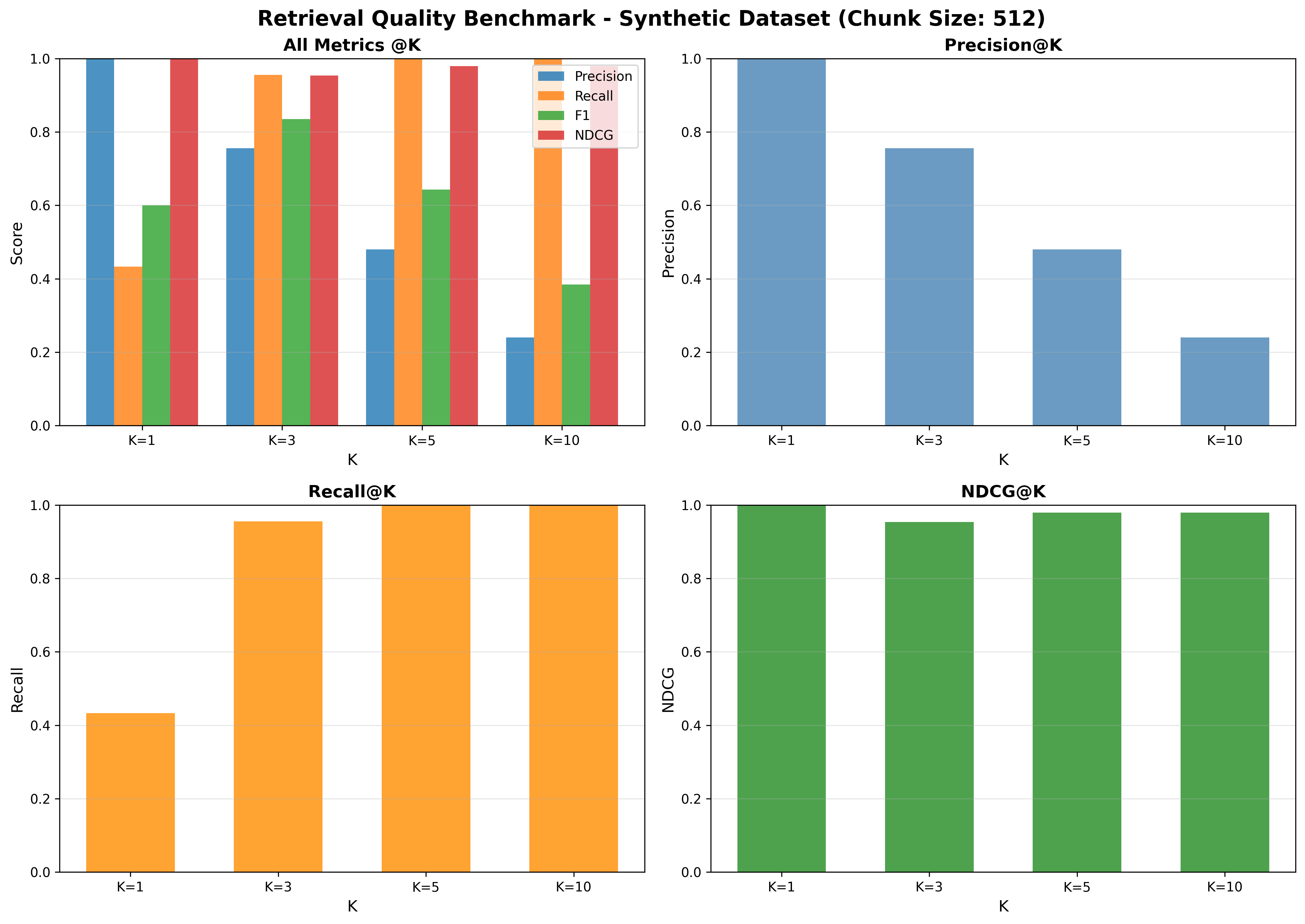
Configuration:
- Dataset: Synthetic
- Chunk size: 512
Quality metrics:
- Precision@k: P@1=1.00, P@3≈0.756, P@5≈0.480, P@10≈0.240
- Recall@k: R@1≈0.433, R@3≈0.956, R@5=1.00, R@10=1.00
- F1@k: F1@1=0.60, F1@3≈0.836, F1@5≈0.643, F1@10≈0.385
- nDCG@k: nDCG@1=1.00, nDCG@3≈0.954, nDCG@5≈0.979, nDCG@10≈0.979
Interpretation:
- Very strong early precision (P@1=1.0) and nDCG across cutoffs indicate effective ranking of the most relevant content.
- Near-perfect recall by k=5 shows top-5 captures essentially all relevant items.
See benchmark_results/retrieval_quality_synthetic.png for the quality curves.
Disclaimer ⚠️: The documents in the dataset used here are relatively short (typically well under 512 tokens).
As a result, a chunk size of 512 effectively corresponds to document-level embeddings — each document was indexed as a single vector.
While this setup is sufficient for small-scale or toy benchmarks, it may not generalize to longer documents where sub-document (passage-level) chunking becomes necessary for finer-grained retrieval.
Future evaluations will include experiments with smaller chunk sizes (e.g., 128–256) and longer document corpora to assess chunk-level retrieval effects.
Features
- Semantic Search: sentence-transformers for accurate semantic similarity search
- Document Chunking: Optional token-based chunking using tiktoken for better search granularity
- Multiple File Formats: Support for PDF, DOCX, and TXT files with OCR capabilities
- Flexible Storage: In-memory or persistent storage with automatic serialization
- GPU Support: CUDA acceleration for faster embedding generation and search
- Precision Control: Support for different precision levels (float32, float16, binary)
- Collection Management: Organize documents into named collections
Installation
Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/capybara-brain346/capybaradb.gitcd capybaradbSetup environment
using venv
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # on macOS/Linux
venv\Scripts\activate # on Windows
pip install -r requirements.txtusing uv
uv syncQuick Start
from capybaradb.main import CapybaraDB
# Create a database with chunking enabled
db = CapybaraDB(collection="my_docs", chunking=True, chunk_size=512)
# Add documents
doc_id = db.add_document("Capybaras are the largest rodents in the world.")
db.add_document("They are semi-aquatic mammals native to South America.")
# Search for similar content
results = db.search("biggest rodent", top_k=3)
for result in results:
print(f"Score: {result['score']:.4f}")
print(f"Text: {result['text']}")
print(f"Document: {result['document']}")
print("---")
# Save the database
db.save()File Processing
CapybaraDB can process various file formats:
from capybaradb.utils import extract_text_from_file
# Extract text from different file types
text = extract_text_from_file("document.pdf")
text = extract_text_from_file("document.docx")
text = extract_text_from_file("document.txt")
# Add the extracted text to the database
doc_id = db.add_document(text)Configuration Options
db = CapybaraDB(
collection="my_collection", # Collection name (optional)
chunking=True, # Enable document chunking
chunk_size=512, # Chunk size in tokens
precision="float32", # Embedding precision: "float32", "float16", "binary"
device="cuda" # Device: "cpu" or "cuda"
)API Reference
Constructor
collection(str, optional): Name of the collectionchunking(bool): Enable document chunking (default: False)chunk_size(int): Size of chunks in tokens (default: 512)precision(str): Embedding precision (default: "float32")device(str): Device for computation (default: "cpu")
Methods
add_document(text: str, doc_id: str = None) -> str: Add a document to the databasesearch(query: str, top_k: int = 5) -> List[Dict]: Search for similar documentsget_document(doc_id: str) -> str: Retrieve a document by IDsave(): Save the database to diskload(): Load the database from diskclear(): Clear all data from the database
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.